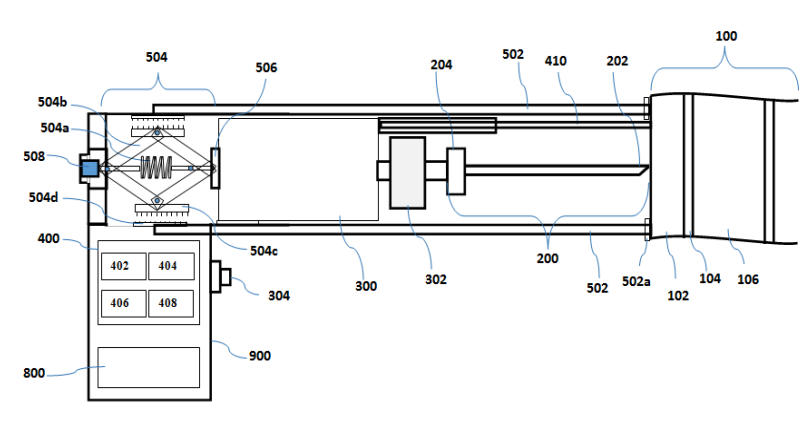
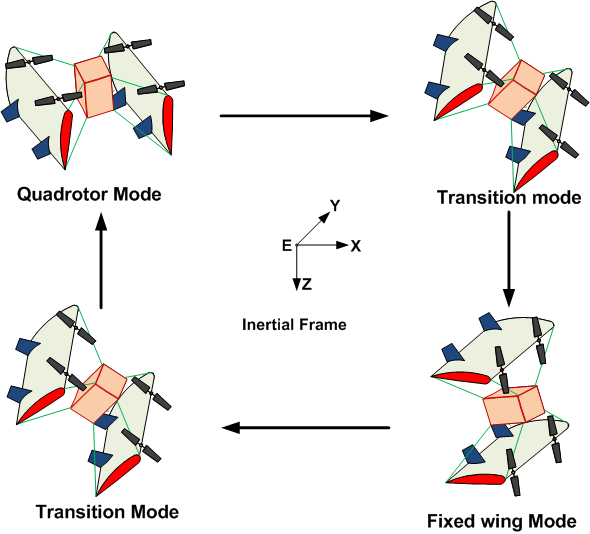
The research was carried out by Gautam Choubey, IITRAM, Kumari Ambe Verma and Krishna Murari Pandey from NIT, Silchar.
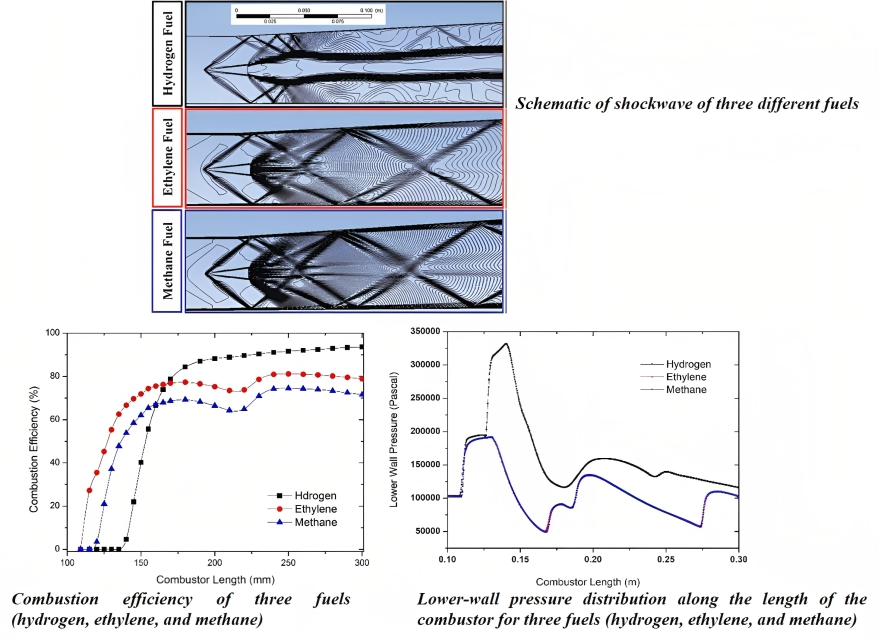
The selection of any space vehicle is considered by analyzing the engine’s power generation. The power gained at the end of each operational cycle in all sorts of space engines is initially dependent on two key factors, i.e., the operating condition of incoming air with working fuel and the selection of working fuel. Other criteria may also affect the engine performance. Therefore, the present article is about the selection of working fuels for supersonic combustion in scramjet engines. Hence, a numerical investigation has been performed by using the computational fluid dynamics approach. The parallel fuel injection strategy has been used to uncover the combustion characteristics. The observation involves flame strength, ignition delay, and mixing length. The three fuels used in this article for comparison are hydrogen, methane, and ethylene. The outcome suggests that ethylene fuel has a lower ignition lag. However, employing hydrogen fuel results in the highest combustion efficiency. Moreover, more robust flames and pressure-field formation with a wider wake region are visualized in hydrogen fuel compared with other fuels.