The Research Team includes Deepak Pandey, Divya Jadav, D. K. Singh, and M. Bandyopadhyay from IITRAM and Other members from PDEU and Hiroshima University, Japan.
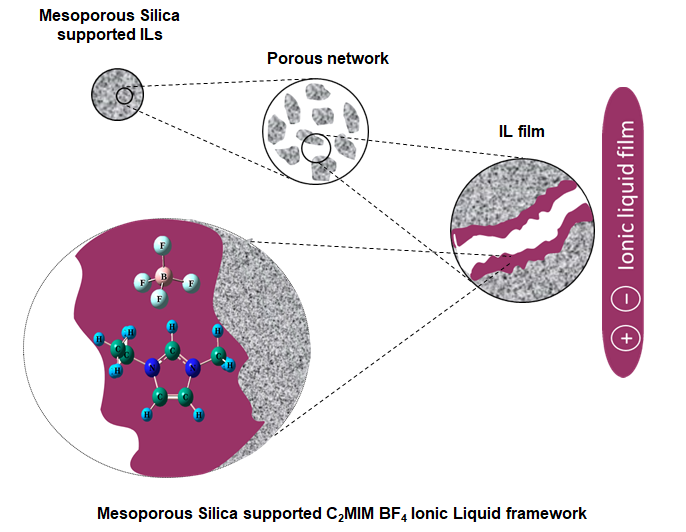
Global concern regarding the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions to mitigate the impact of global warming has intensified due to the alarming concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere. In this context, researchers have focused on the development of supported-ionic liquids (SILs), which involve the infusion of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (C2mim BF4) ionic liquid (IL) into ordered mesoporous silica (MS) matrices. The aim is to create SIL-based membranes (SILMs) suitable for advanced gas separation technology.
By employing a solution casting technique, SILMs membranes based on Pebax-1657 were also fabricated to evaluate their gas separation performance. The C2mimBF4/MCM-48 membrane exhibited notably higher permeability for CO2 in both single gas and mixed gas experiments. These findings were further corroborated by density functional theory (DFT) analysis, specifically by examining complexation energies (Ec). The results demonstrated the strong affinity of these SILMs membranes towards CO2 and CH4 gases, respectively. Moreover, a meaningful correlation was established between the empirical and theoretical findings.
This research provides valuable insights into the potential application of SILMs for CO2 separation and underscores their promising role in addressing the pressing global challenge of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.